Are you struggling to grasp the complexities of English tenses? Look no further! In this text, we will investigate into the world of tenses, providing you with a comprehensive tense chart and examples for each of the 12 tenses in English. Whether you’re a student preparing for exams or simply looking to enhance your language skills, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to excel.
Mastering tenses is essential for effective communication in English. Without proper understanding and usage of tenses, your intended meaning may be lost or misunderstood. That’s why we’ve compiled this detailed tense chart, complete with examples, to help you navigate the intricacies of verb forms and tenses in English grammar.
Key Takeaways
- Mastering the complexities of verb tenses in English is crucial for effective communication.
- English grammar encompasses 12 basic tenses, each with its own unique forms and uses.
- Using the correct tenses ensures clear and accurate communication, while incorrect usage can lead to confusion or misinterpretation.
- The four aspects of verb tenses are simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive, and understanding their distinctions is essential.
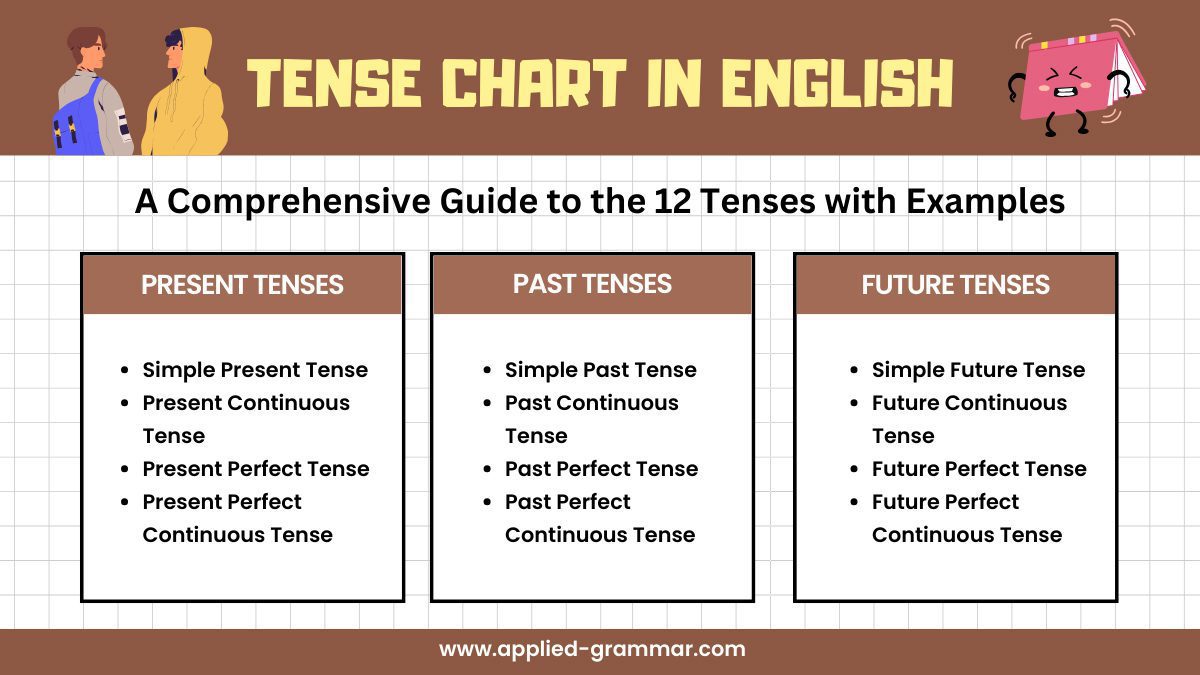
- Present tenses in English include the simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous.
- Past tenses in English include the simple past, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous.
- Future tenses in English include the simple future, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous.
Understanding Tenses in English
To effectively communicate and understand the English language, it is crucial to master the complexities of verb tenses. Verb tenses indicate the time frame in which an action takes place – whether it is in the past, present, or future. English grammar encompasses 12 basic tenses, each with its own unique forms and uses. Let’s jump into a deeper understanding of these tenses to enhance your language skills.
What are Tenses?
Tenses in English grammar are used to express actions that have occurred in the past, are happening in the present, or will occur in the future. Identifying the correct tense of a verb is essential for conveying accurate meaning in your sentences. Verb tenses are further divided into four aspects: simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive. Understanding the distinctions between these aspects will provide you with a strong foundation in English grammar.
Importance of Using Correct Tenses
Using the correct tenses is vital for effective communication. It ensures that your message is clear and properly conveys when an action occurred or will occur. Incorrect usage of tenses can lead to confusion or misinterpretation. For example, using the wrong tense in a sentence might give the impression that an action happened in the present when it actually took place in the past. Mastering the correct usage of tenses will enhance your fluency and accuracy in the English language, enabling you to express yourself more effectively.
To summarize, a firm grasp of English verb tenses is crucial for effective communication. Understanding the different tenses and their uses allows you to accurately convey the timing of actions in your sentences. By using the correct tenses, you can enhance your language skills, ensure clear communication, and avoid confusion. Keep reading to explore the various types of tenses and their examples in our comprehensive tense chart.
Types Of Tense
Understanding the different types of tenses in English grammar is essential for effective communication. In this section, we will explore the 12 tenses in English with examples, providing you with a comprehensive overview of each tense and its usage.
1. Simple Present or Present Indefinite
This tense is used to describe actions that are happening in the present, habitual actions, general truths, and scheduled events.
Example: “You play the guitar every day.”
2. Present Continuous
The present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are happening at the moment of speaking or actions that are in progress.
Example: “She is having a conversation with her friend.”
3. Present Perfect
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions that were completed in the past but have a connection to the present.
Example: “I have visited London multiple times.”
4. Present Perfect Continuous
This tense is used to describe actions that started in the past, continued up until the present, and may continue into the future.
Example: “They have been studying for five hours.”
5. Simple Past or Past Indefinite
The simple past tense is used to describe completed actions in the past.
Example: “He played football yesterday.”
6. Past Continuous
The past continuous tense is used to describe actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past.
Example: “We were watching a movie when it started raining.”
7. Past Perfect
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another past action.
Example: “She had already left when I arrived.”
8. Past Perfect Continuous
This tense is used to describe actions that started in the past, continued for a period of time, and were still ongoing at a specific point in the past.
Example: “They had been traveling for two weeks before they reached their destination.”
9. Simple Future or Future Indefinite
The simple future tense is used to describe actions that will happen in the future.
Example: “I will send you the information tomorrow.”
10. Future Continuous
The future continuous tense is used to describe actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future.
Example: “At this time tomorrow, she will be attending a meeting.”
11. Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used to talk about an action that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
Example: “By tomorrow morning, I will have finished writing my essay.“
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous differs slightly from the future perfect. It describes an action that will have been ongoing up to a specific point in the future.
Example: “By the time you arrive, I will have been working on this project for three hours.”
Present Tenses
In English grammar, the present tense refers to actions or events that are currently happening or occurring in the present moment. Understanding the different present tense forms is essential for effective communication and writing. In this section, we will explore the four types of present tenses: the simple present tense, present continuous tense, present perfect tense, and present perfect continuous tense.
Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is used to describe general truths, habits, repeated actions, and permanent situations. It is formed by using the base form of the verb in the affirmative, followed by the subject. Here are a few examples:
- You study English every day.
- She goes to the gym regularly.
- The sun rises in the east.
Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is used to express actions that are happening at the time of speaking or actions that are temporary. It is formed by using the helping verb “be” (am, is, are) followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- You are studying for your exam.
- She is dancing at the party.
- They are playing football in the park.
Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions that started in the past and have a connection to the present. It is formed by using the helping verb “have” or “has” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
- They have finished their assignments.
- She has traveled to many countries.
- We have seen that movie before.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that started in the past, have a connection to the present, and are still ongoing. It is formed by using the helping verb “have” or “has” followed by “been” and the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
- He has been working on the project for hours.
- They have been waiting for the bus since morning.
- We have been studying English grammar all day.
Understanding the different present tenses in English grammar is essential for effective communication. Practice using these tenses in different contexts to improve your writing and speaking skills. In the next section, we will explore the past tenses in English grammar.
Past Tenses
In English grammar, the past tense refers to the form of a verb that expresses an action or event that has already happened or occurred in the past. There are four main types of past tenses, each serving a different purpose in communication and writing. In this section, we will explore each of these past tenses and provide examples to help you understand their usage and formation.
Simple Past Tense
The Simple Past Tense is used to describe events that began and ended in the past, and are completely finished. Most verbs can be made past tense by adding “ed” or “d” to the end of a present tense verb, such as “liked” and “watched”. But, there are also irregular verbs that have unique past tense forms. For example, “go” becomes “went” and “think” becomes “thought”.
Examples:
- We lived in Australia.
- He went to the gym.
- Kamala sang a song.
Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense is used to describe events that began in the past, continued for a length of time, and ended in the past. To form this tense, we use the helping verb “was/were” followed by the main verb with “-ing” added to it.
Examples:
- We were going to Australia.
- He was going to the gym.
- Kamala was singing a song.
Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe a past event that occurred before another past event. It shows that one action happened earlier than another action in the past. To form this tense, we use the helping verb “had” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Examples:
- We had gone to Australia.
- He had gone to the gym.
- Kamala had sung a song.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe an event that began in the past, continued for a length of time, and was in progress when another past event happened. To form this tense, we use the helping verb “had been” followed by the verb with “-ing” added to it.
Examples:
- You had been playing all day.
- I had been working on this project.
- She had been reading story books.
Understanding the different past tenses is crucial for effective communication and writing in English. By practicing these tenses in different contexts, you’ll be able to improve your language skills and convey your thoughts and experiences with clarity and precision. So, next time you want to talk about events that have already happened, remember to choose the appropriate past tense.
Future Tenses
In English grammar, the future tense refers to actions or events that are expected to happen or occur in the future. There are four types of future tenses that are used to express various aspects of future actions. Let’s explore each of these tenses in detail:
Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is used to describe events that haven’t happened yet, but are expected to occur in the future. It is commonly used to express intentions, predictions, or promises. To form the simple future tense, we use the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” followed by the base form of the verb. Here are a few examples:
- This year, you will go to Disneyland.
- They will come to the party tomorrow.
- I shall go to Japan next month.
Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense is used to talk about actions that will start in the future and continue for a specific amount of time. It is formed using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “be” and the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. This tense is often used to describe ongoing actions or plans. Here are some examples:
- We will be buying a house next year.
- They will be going to college next semester.
- She will be starting her new job next week.
Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used to describe a future event that will be completed before another future event. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” followed by “have” and the past participle of the verb. This tense is often used to express a future action that will be finished at a specific time. Here are a few examples:
- By the time we arrive, they will have left Australia.
- He will have gone to the gym before dinner.
- She will have sung a song by the end of the concert.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense is used to describe a future action that will have started, continued, and still be in progress when another future event occurs. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “have been” and the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. This tense emphasizes the duration or length of an action in the future. Here are some examples:
- By the time they arrive, we will have been visiting Australia for two weeks.
- He will have been going to the gym for five years next month.
- Kamala will have been singing a song for hours before the show ends.
It is important to understand the different future tenses to effectively communicate about future actions or events. Practice using these tenses in various contexts to improve your language skills and accuracy. So, the next time you talk about future plans, remember to choose the appropriate future tense to convey your intended meaning.
Conclusion
Mastering the 12 tenses in English is essential for effective communication and writing. In this text, we have explored the different tenses and their usage, starting with the present tenses and moving on to the past and future tenses.
By understanding the various forms of each tense and practicing them in different contexts, you can enhance your language skills and express yourself more accurately. Whether you are talking about current events, past experiences, or future plans, choosing the appropriate tense is crucial.
Remember, language is dynamic, and the more you practice, the more confident you will become in using the different tenses. So, keep practicing and incorporating the 12 tenses into your everyday conversations and writing.
By mastering the tense chart in English, you will be able to convey your thoughts and ideas with precision and clarity. So, keep learning, keep practicing, and soon, you’ll be a master of the English tenses!